From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject. (October 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Myelin incisure | |
|---|---|
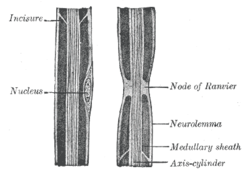
Diagram of longitudinal sections of medullatednerve fibers. (Incisure labeled at upper left.)
| |
| Identifiers | |
| Code | TH H2.00.06.2.03015 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | 12447772 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Myelin incisures (a.k.a. Schmidt-Lanterman clefts, Schmidt-Lanterman incisures, clefts of Schmidt-Lanterman, segments of Lanterman, medullary segments), are small pockets of cytoplasm left behind during the Schwann cell mylenation process. They arehistological evidence of the small amount of cytoplasm that remains in the inner layer of the myelin sheath created by Schwann cellswrapping tightly around a nerve.
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS) axons can be either myelinated or unmyelinated. Myelination refers to the insulation of an axon with concentric surrounding layers of lipid membrane (myelin) produced by Schwann cells. These layers are generally uniform and continuous (similar in structure to a fruit roll up), but due to imperfect nature of the process by which Schwann cells wrap the nerve axon, this wrapping process can sometimes leave behind small pockets of residual cytoplasm displaced to the periphery during the formation of the myelin sheath. These pockets, or "incisures", can subdivide the myelinated axon into irregular portions. These staggered clefts also provide communication channels between layers by connecting the outer collar of cytoplasm of the Schwann cell to the deepest layer of myelin sheath.
References[edit]
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links[edit]
- Histology image: 22801loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire